The Value of Investing in an Inflationary environment
Commentary

Inflation has been a major discussion point following the pandemic, as economies around the world recover from the decline in economic activity caused by the spread of the Covid-19 virus and its associated lockdowns. While inflation is normal and necessary for economic growth, significantly elevated levels can disrupt stability and create financial challenges. Inflation in the United States accelerated to a forty-year high of 7.5% year on year in January 2022. The rest of the world also continues to be affected by elevated inflation rates including Trinidad and Tobago. As a result, it is vital to have a clear understanding of inflation as well as the strategies that can be taken from an investment perspective in order to mitigate its negative effects.
What is Inflation?
Inflation is the decline of purchasing power of a given currency over time. A quantitative estimate of the rate at which the decline in purchasing power occurs can be reflected in the increase of an average price level of a basket of selected goods and services in an economy over some period of time. The rise in the general level of prices, often expressed as a percentage, means that a unit of currency effectively buys less than it did in prior periods.
While it is easy to measure the price changes of individual products over time, human needs extend beyond one or two such products. Individuals need a diversified set of products as well as a host of services in order to live comfortably. These include commodities like food grains, metal, fuel, utilities, transportation and healthcare services.
Inflation aims to measure the overall impact of price changes for a diversified set of products and services, and allows for a single value representation of the increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. The most commonly used inflation indices in the United States are the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index (PCE). The change in the Retail Price Index (RPI) is the major inflation statistic used in Trinidad and Tobago.
The General Causes of Inflation
While there are many factors that can lead to inflation in an economy, the causes of inflation generally comprise two main categories, demand-pull inflation and cost-push inflation. Demand-pull inflation occurs in a strong or strengthening economy. As economic activity picks up, the labour market becomes stronger and incomes may increase, which results in an overall increase in the demand for goods and services. In some cases, consumer demand may exceed the supply of goods and services which leads to price increases.
Cost-push inflation is caused by an increase in the cost of goods used in the manufacturing and production of goods and services. For example, if the cost of raw materials goes up significantly and businesses are unable to absorb this cost increase, it will be passed on to the consumer in the form of higher prices. Natural disasters, supply chain disruptions and rising energy prices may all result in cost push inflation.
How the Pandemic Fueled Inflation
The current inflationary environment has been caused by a combination of both demand pull and cost push inflation. As economies reopened and employment gradually increased, there was greater demand for goods and services. Additionally, many households accumulated savings during the pandemic and are now willing to spend this additional cash in order to satisfy pent up demand. Many governments throughout the world also provided additional fiscal support in order to ease the financial burdens of citizens. This also contributed to the additional liquidity which fueled demand-pull inflation.
On the supply side many companies decreased output during the pandemic as the virus surged in many countries, limiting production. With the surge in demand following the pandemic, producers were unable to respond quickly to this added demand. Additionally, many emerging market economies where the majority of raw materials are sourced for production were still recovering from the pandemic and as a result there were shortages of vital production inputs. These factors along with increased shipping demand, increased the cost of goods thereby contributing to cost push inflation.
Investing to mitigate Inflation
A disciplined investor can plan for inflation by investing in asset classes that outperform or keep up with the market during inflationary periods. To effectively protect your investment portfolio against inflation, investors can select assets that appreciate in value at a greater rate than the current rate of inflation or pay a variable interest rate. Investing in tangible assets such as gold, commodities and real estate, floating-rate bonds and equities are also options.
Commodities and gold are two types of physical assets and have intrinsic worth, unlike currencies whose value is backed by real assets. The prices of such assets tend to rise in value alongside inflation. In the local economy, it may not be possible to have a direct investment in gold or commodities, however, investors can still invest in these assets through an exchange traded fund (ETF) or into real estate via a real estate investment trust (REIT).
Fixed Income or bonds are debt instruments offered by companies and governments as a way of raising capital. Bonds usually offer a fixed payment over its lifetime, thus investors will receive a stated amount and may lose value in an inflationary environment. Bonds with fluctuating or variable interest rates allow the investors to earn a higher income as the interest rate rises.
Equities are issued by a public limited company and are traded on the stock market. When you invest in an equity, you buy a share in a company, and become a shareholder. Equities have the potential to yield returns in two ways. An equity investor can receive capital growth through increases in the share price, and can also receive income in the form of dividends. Neither of these is guaranteed and there is always the risk that the share price will fall below the level of the initial investment. On the upside however, provided that a company’s profits grow over time, its stock price should climb. Additionally, in an inflationary environment an investor may wish to choose companies that have pricing power in their industry, so as their own costs rise, they can raise their prices accordingly in order to protect their margins and by extension the return to their shareholders.
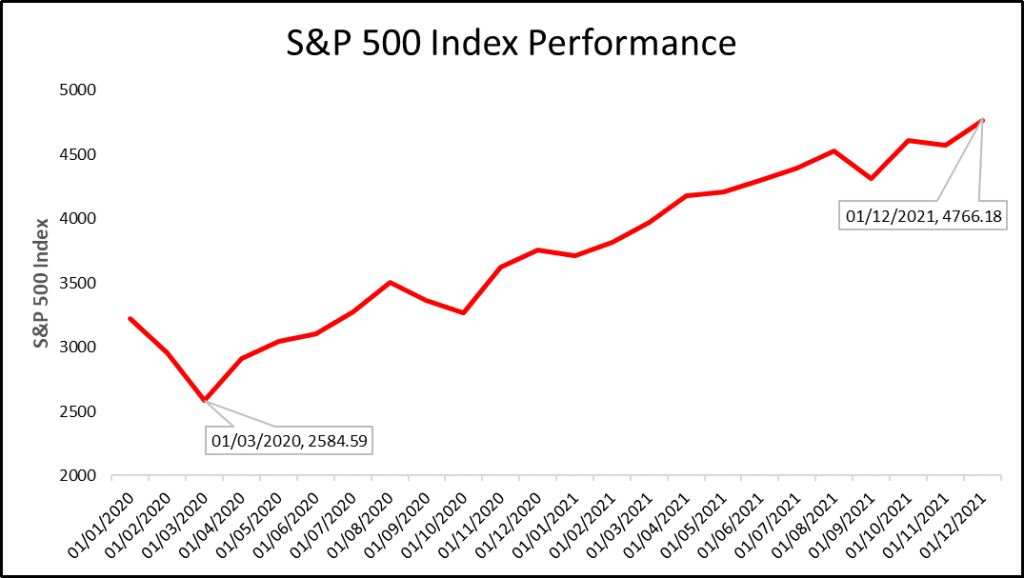
Traditionally, equities have the potential to generate greater returns than that of fixed income but are also a riskier asset class. The S&P 500 Index for example would have increased by 26.89% in 2021. This performance would have significantly outpaced the actual rate of US Inflation which stood at 7% at the end of 2021. The US equity market continues to be the largest most liquid market in the world.
Conclusion
Given the current environment, adopting a suitable investment strategy is vital in order to prevent the erosion of purchasing power due to inflation. While all investments carry varying degrees of risk, a diversified investment portfolio containing real assets, variable rate bonds and equities may serve to effectively manage inflation risk. Additionally, it is vital to identify the sectors that present the most upside opportunity in the future, for example with the global transition to renewable energy having exposure to this sector may provide significant returns in the coming years. Having a discussion with an investment advisor may also assist in designing a portfolio of investments that suits the risk profile and time horizon of a potential investor.
DISCLAIMER
First Citizens Bank Limited (hereinafter “the Bank”) has prepared this report which is provided for informational purposes only and without any obligation, whether contractual or otherwise. The content of the report is subject to change without any prior notice. All opinions and estimates in the report constitute the author’s own judgment as at the date of the report. All information contained in the report that has been obtained or arrived at from sources which the Bank believes to be reliable in good faith but the Bank disclaims any warranty, express or implied, as to the accuracy, timeliness, completeness of the information given or the assessments made in the report and opinions expressed in the report may change without notice. The Bank disclaims any and all warranties, express or implied, including without limitation warranties of satisfactory quality and fitness for a particular purpose with respect to the information contained in the report. This report does not constitute nor is it intended as a solicitation, an offer, a recommendation to buy, hold, or sell any securities, products, service, investment or a recommendation to participate in any particular trading scheme discussed herein. The securities discussed in this report may not be suitable to all investors, therefore Investors wishing to purchase any of the securities mentioned should consult an investment adviser. The information in this report is not intended, in part or in whole, as financial advice. The information in this report shall not be used as part of any prospectus, offering memorandum or other disclosure ascribable to any issuer of securities. The use of the information in this report for the purpose of or with the effect of incorporating any such information into any disclosure intended for any investor or potential investor is not authorized.
DISCLOSURE
We, First Citizens Bank Limited hereby state that (1) the views expressed in this Research report reflect our personal view about any or all of the subject securities or issuers referred to in this Research report, (2) we are a beneficial owner of securities of the issuer (3) no part of our compensation was, is or will be directly or indirectly related to the specific recommendations or views expressed in this Research report (4) we have acted as underwriter in the distribution of securities referred to in this Research report in the three years immediately preceding and (5) we do have a direct or indirect financial or other interest in the subject securities or issuers referred to in this Research report.